Learn SEO Tutorial: Step-By-Step SEO Guide for Beginners
- Section 1: Introduction to Search Marketing
- Section 2: Internal SEO (On-page SEO)
- Section 3: External SEO (Off-page SEO)
If you finish reading this entire guide…
You will understand SEO better than 90% of beginner internet marketers out there.
Section 1: Introduction to Search Marketing
When you enter a keyword into any search engine, you instantly get results (webpages) that are closely related to or match your search query.
To an average user, this doesn’t seem like anything out of the ordinary. But to many businesses, being right in front of their customers every time they show interest in a related product or service can mean big bucks… and I mean steady, monthly recurring income.
First, what is SEO?
What is SEO?
SEO or Search Engine Optimisation is the process of optimising a website’s visibility on the organic search engine results pages (SERPs) for a target set of keywords/phrases.
The higher the position of a webpage on the organic search results pages, the more “visible” the page will be.
Related: What is SEO Marketing and How it Works
How do search engines work?
Algorithms
Search engines use algorithms to calculate how worthy a page is to a relevant search query. There are hundreds of factors (Google uses over 200 ranking factors) that are used to calculate the authority of a webpage, and PageRank (based on a scale of 0 – 10) is one of them.
Google assigns PageRank to every webpage it crawls. When another website links to your website, some of its PageRank is passed on to you. The more sites there are out there linking to you, the higher your PageRank will be and the more trustworthy your site will look to search engines.
Crawling
Search engines use bots or “spiders” to crawl billions of pages across the web by following links they find from billions of pages around the web.
Indexing
Search engines then store the information it collects into its index.
Ranking
When a search query is entered, a search engine digs into its index for pages matching the user’s search query, then sorts and displays the most relevant results to the user.
The order in which the pages are displayed are calculated by search engine algorithms, taking into account hundreds of ranking factors. Each page is then given a ranking score.
In order to rank highly on the search engines, your site needs to score higher than all the other sites that are eligible to show up for a relevant search query.
However, be warned that if you engage in shady methods and try to deceive the search engines, you will get yourself burned. Google is very strict on sites that try to manipulate their rankings and if you’re caught doing so, your site will get penalized and removed from the SRPs a.k.a. the “Google Slap”.
Google Major Algorithm Updates: Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird
Every year, Google changes its algorithms some 500 times, that’s 1 – 2 times on average each day. Every once in a while, Google rolls out a major algorithm update, and when they do so, many sites suffer a drop in rankings while many others enjoy a raise in rankings.
Panda (2011)
Lower the rankings of low-quality sites.
Penguin (2012)
Decrease rankings of sites that engage in black-hat SEO.
Hummingbird (2013)
Relevancy and knowledge graph update (Semantic search).
RankBrain (2016)
Machine learning to improve search result quality.
BERT (2019)
A revolutionary natural language processing model to better understand the meaning and intent of user search queries.
Read Moz.com for more details on the Google algorithm change history.
What are some Black-Hat SEO techniques?
Cloaking – Displaying different results to search engines and users with the intent of manipulating SE rankings.
Mass acquisition of low quality links in a very short period of time.
Overuse of keywords in article title and/or content body in a weak attempt to boost rankings for relevant target keywords or key phrases.
View Google’s content guidelines on various link schemes to avoid.
How do you do White-Hat SEO?
Well, just avoid doing Black-Hat SEO and you’ll be doing White-Hat SEO!
We will cover essential on-page SEO such as image optimisation, good internal linking structure, quality and uniqueness/originality of the content, and more later on.
SEO is divided into two parts – Internal SEO, and External SEO
To give you a better picture of SEO, let’s pretend you’re building a new shopping mall.
Before constructing your shopping mall, you first have to take into consideration internal and external factors. Most importantly, you have to take into consideration what makes a great visitor experience.
Internally, what is your shopping mall about? Is the theme of your shopping mall unique? Are different shop themes categorised into different levels? Do visitors find it easy to find their way around the mall?
Externally, have you taken the steps to put the word out that your shopping mall exists? Is your shopping mall listed in map directories, roadside signboards, or brochure stands in neighbouring malls?
If you’ve taken good care of both internal and external factors, chances are your mall will be booming with business.
Similarly, before building your website, have you considered…
Internally, what is your website about?
If you don’t even know what your site is about, it’s very likely search engines won’t as well.
Is your site’s theme unique in any way?
Search engines love unique content and will reward high quality content. On the other hand, duplicate or scraped content will not do well on the SRPs.
Are your content themes properly organised and well interlinked?
Websites that have clean site structure with content properly organised into different categories enable search engine spiders to easily crawl through internal pages and index them appropriately.
Do users find it easy to navigate through your site?
Search engines can detect whether users will find it easy or not to navigate through a site. A well-organised site provides a good user experience, which is precisely what search engines were built for in the first place. Sites with a clean structure and a clear purpose tend to rank higher on the SRPs.
Externally, have you made the effort to communicate with other webmasters in your related niche?
Search engines encourage you to actively participate in your community and provide value. Providing value to your community boosts your reputation and increases the chances of attracting inbound links to your site.
Are the chances of them linking to your site high?
Have you taken the initiative to share your content through popular social networking sites? If your content is interesting, share-worthy, and of high quality, chances are you will attract a lot of inbound links.
Do you have a lot of other sites linking to your site, increasing your popularity?
The more inbound links (backlinks) you acquire, the more trustworthy search engines will deem your content.
If you answered yes to all the above questions, you’re doing great SEO!
Search engines were built by humans, for humans. Focus your site on delivering a great user experience and you can rest assure that your site will do well on the search engines.
How Can SEO Enhance Your Overall Digital Marketing Strategy?
Improve Overall User Experience On Your Site
Having good knowledge on the topic of internal SEO and on-page ranking factors will help you better organise your site structure (arranging different categories according to specific themes) to deliver a great user experience, construct a good internal linking structure for better user navigation, and make your site more engaging, resulting in higher conversion rates.
Increase Offline Sales
Help your customers find you better with local directory listings such as Google Places, Yelp, and Street Directory.
80% of internet consumers in the product awareness stage conduct research online before deciding whether or not to make a purchase.
Online Reputation Management
Protecting your online reputation is getting more and more important these days as more and more consumers search for brand names on search engines instead of just entering the direct url i.e. “brandname.com” and the last thing you want them to see is a bad review of your company ranking above your company website.
Read: What is an SEO Strategy and Why You Need an Integrated Marketing Strategy?
Section 2: Internal SEO
Internal Optimisation Process
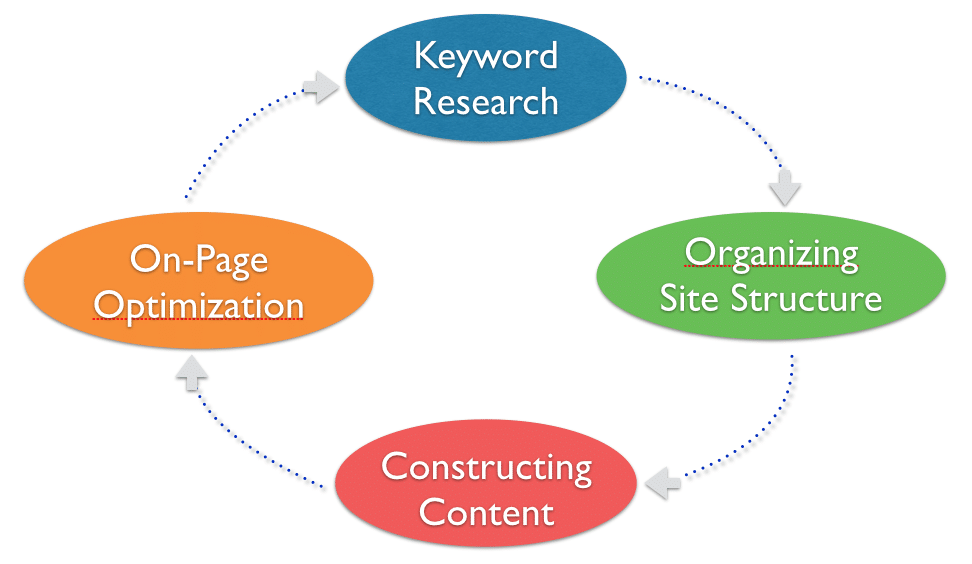
There are 4 main steps when it comes to internal SEO – Keyword Research, Organising Site Structure, Constructing Content, and On-Page Optimisation. Let’s go through each step one by one.
Step 1: Keyword Research: Competitive Market Research
Long-tail keywords
When starting out, you want to look out for as many long-tail keywords as you can. Long-tail keywords (more words) are not as difficult to rank highly for as generic keywords (fewer words). Long-tail keywords are also more specific to a user search query and are more likely to result in a conversion.
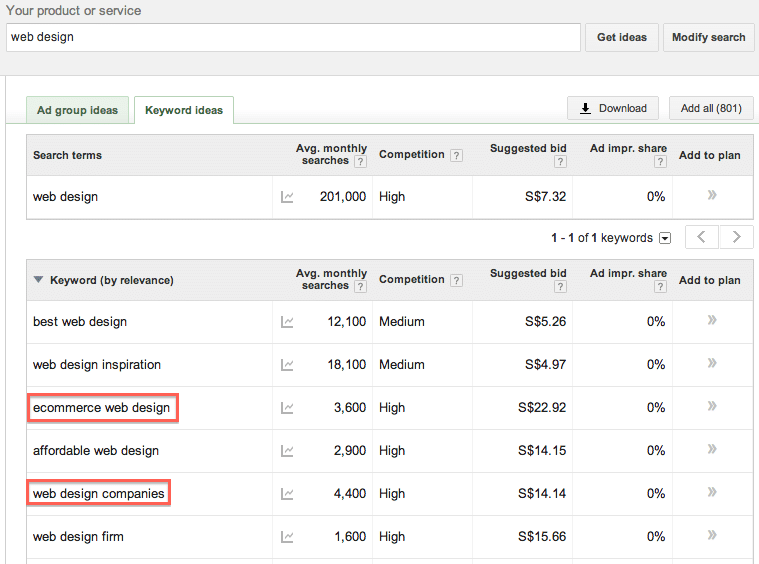
Start with a generic theme. For example, “Website Design”, if you are a web designer, then expand your list of keywords from there i.e. “E-commerce Web Design”, “Affordable Web Design”, etc…
Use the Google Keyword Planner to conduct your SEO keyword research.
Researching for new keywords
If you’re building a brand new site, keyword research should be the first thing you do before filling up your site with content. If you’re already running a site, it is also good practice to constantly expand your list of target keywords.
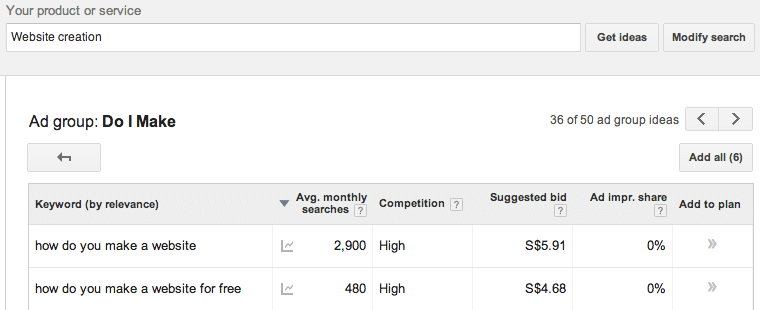
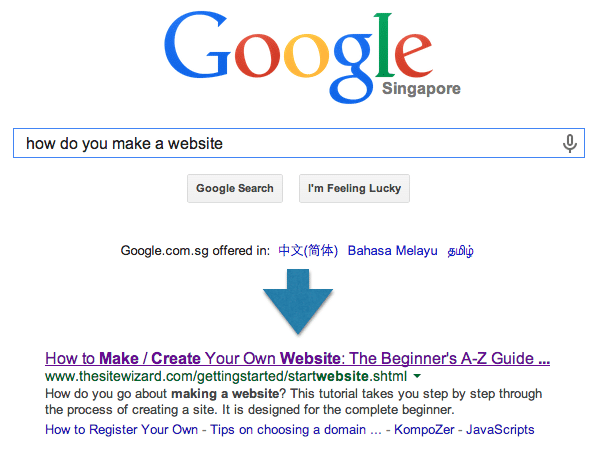
Keyword research can help you discover what consumers are actually searching for. When you know what your consumers are looking or asking for, you can better design your content to answer their queries by speaking to them in their language. For example if you know people are searching for the exact key phrase “How do you make a website”, you can create an article titled “How to Make/Create a Your Own Website”.
You can develop a variety of content ideas just by going through your list of keywords.
You want to build a long list of keywords before you start constructing and organising your articles.
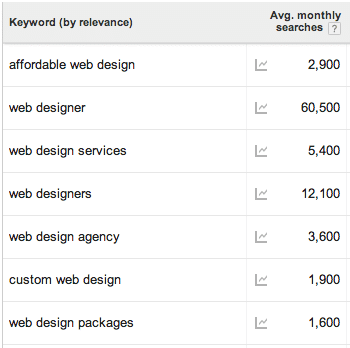
Below is an example of a list of keywords generated by a web design firm:
Referencing the above list of keywords, a web design firm will have a good idea of which keywords to optimise for and how to structure their website (SEO Siloing). i.e.
Web design packages
=> custom web design
=> affordable web design
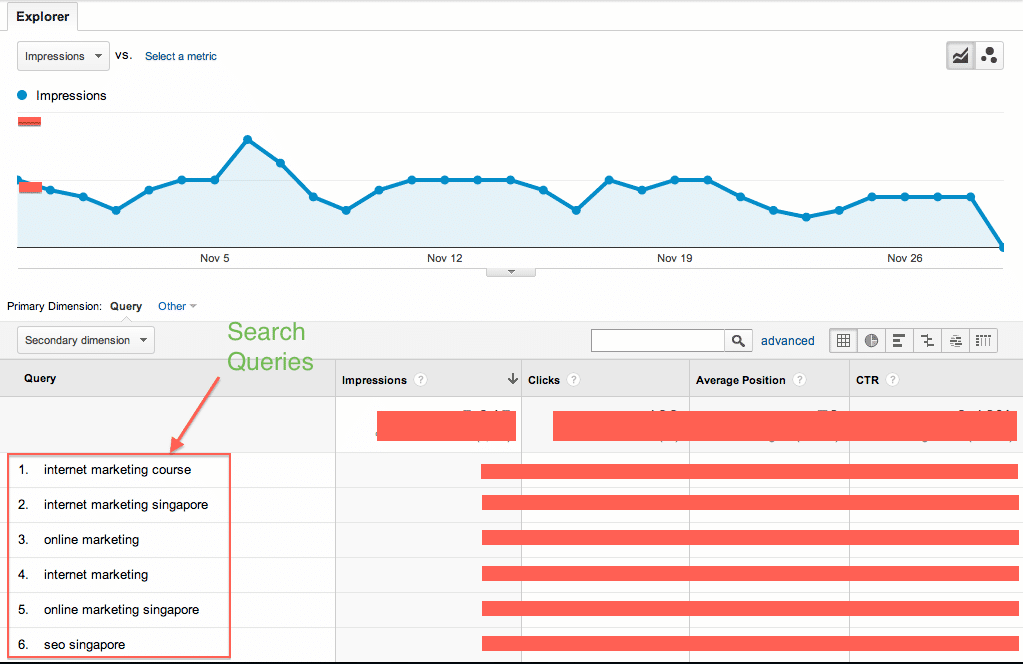
Analysing existing keywords that your site is already ranking for
If your site is already up and running for some time, you may want to sign up for Google Analytics (if you haven’t already) and check which keywords your current visitors have been using to get to your site. These keywords in your analytics report are likely the keywords that you are already ranking well for, so you want to put more focus on them first.
Once you’ve identified these keywords, the next step is to focus your internal optimisation efforts on these keywords in the next 3 steps — Organising site structure, constructing content, and on-page optimisation.
Step 2: Organising Site Structure: SEO Siloing (Website Theming)
Remember the shopping mall example? Let’s say you love electronic products and your focus is on building the largest electronics shopping centre in town. If your shopping mall has a specific theme i.e. Electronics Centre and all retail shops in your shopping mall are dealing with electronic goods and categorised into different electronic themes at different levels, as opposed to a generic theme i.e. Downtown Shopping Mall with only a few electronic retail shops, chances are your Electronic Centre will stand out in consumers’ minds whenever they think of buying any electronic products.
Similarly, Google and other search engines like Yahoo! & Bing give preference to theme-specific sites when deciding which results to show for a relevant user search query. But if you’ve already built a multi-themed site and want to rank for themed-specific search terms, it’s not the end of the world.
Introducing SEO Siloing/Website Theming/Content Hubs
As mentioned, Google, Yahoo! & Bing favour sites that are theme-specific. Sites with clear structures, relevant high-quality content, and written in clean and neat code (no flash, minimal javascript, use HTML for most of their site) also tend to do very well in the search engines.
Therefore it is safe to assume that you do not need to have only one topic on any one site in order to rank well for a theme-specific keyword.
Another scenario would be a box of macarons.

1st Scenario: A box of Green Macarons, Brown Macarons, and Red Macarons mixed together.
In this scenario, search engines will likely classify this site as “A box of Macarons”.
2nd Scenario: A box of Green Macarons, A box of Brown Macarons, A box of Red Macarons all separated into different boxes.
In the second scenario, search engines will likely classify these 3 sites as… A box of Green Macarons, A box of Brown Macarons, A box of Red Macarons.
3rd Scenario: A box of Green Macarons, Brown Macarons, and Red Macarons organised into separate sections.
In the third scenario, search engines can clearly distinguish between the 3 different themes of macarons and index them according to their specific themes.
So what is a silo in terms of SEO?
A silo is a group of theme-specific subjects or topics in a website.
What is SEO siloing and why is it important in search engine optimisation?
SEO siloing is the process of organising different groups of content topics into specific categories. Much like a bookstore organising different genres of books into different sections.
In terms of SEO, this organisational structure is very important in order for the search engines to understand the theme and intention of your website and rank your site accordingly.
There are two methods of SEO siloing. Physical siloing and Virtual siloing.
Physical Siloing
Physical siloing is organising similar-topic content into similar categories or directories. Much like organising your computer files into different folders.
Virtual Siloing
Virtual siloing on the other hand, is utilising internal links to relate subject-specific content to one another. i.e. linking from one blogpost to another, whereby both blogposts exist in different directories or categories.
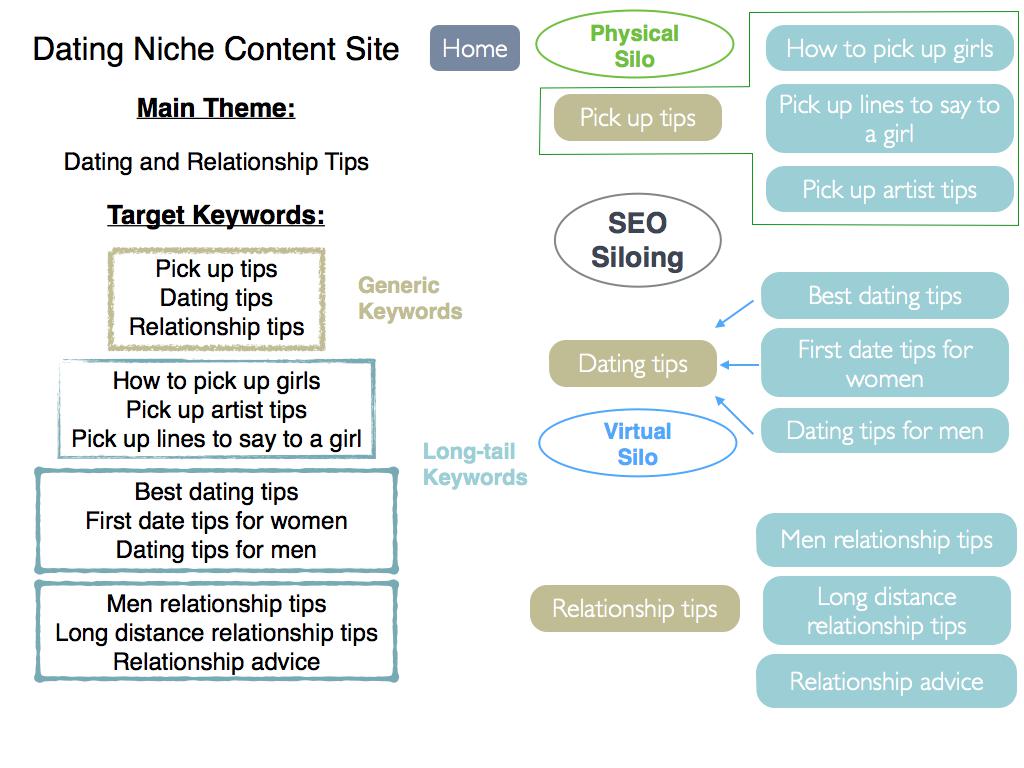
Diagram of a Silo-ed Site Structure:
Above example: How a dating niche content site organises its site structure.
Reference:
Bruce Clay on SEO Siloing – https://www.bruceclay.com/seo/silo/
Sitemaps
You also want to create a HTML or XML sitemap and submit it to the search engines. It’s recommended to include a HTML sitemap for your visitors to refer to and an XML sitemap to submit to the search engines.
You can create your sitemap using free sitemap generator tools like https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/
In order to submit your sitemap to Google, you will need a Google Webmaster Tools account.
Step 3: Constructing Content: Creating Your Landing Pages
What are landing pages?
Landing pages are the pages that your visitors directly land onto when they click on a search result. It is important that your landing pages capture your visitor’s attention and lead them to the inner pages of your site.
If your landing page doesn’t answer the search query or isn’t compelling enough and majority of visitors landing on your landing page click the “back” button and go back to the search results, you’d likely see your rankings dipping over time.
There are three steps you should follow in order when constructing your landing pages:
1) Plan your article using your researched keywords.
2) Write your article, keeping your keywords in mind.
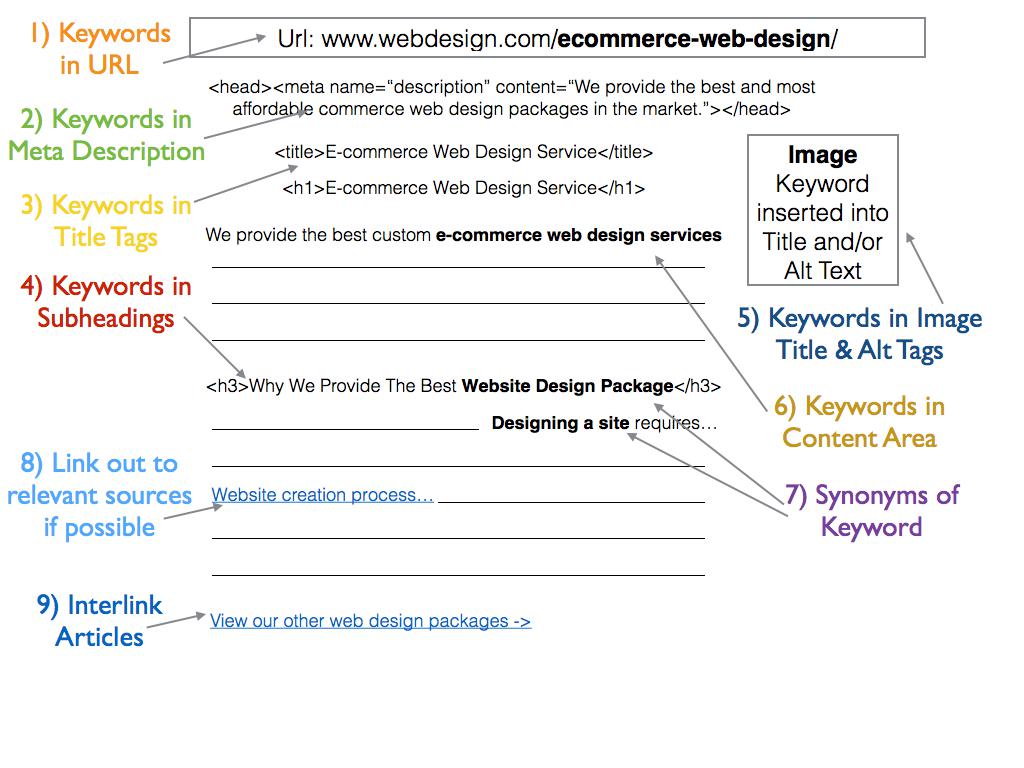
3) Insert your keywords where appropriate. In the title tag, content body, image alt tags, and subheadings.
Step 4: On-Page Optimisation: On-Page SEO Factors
Once you’ve completed steps 1 to 3, you’re ready for step 4 of the internal SEO process.
Refer to the above diagram when performing on-page SEO, or SEOgoodguy’s Make a Blogpost SEO Friendly article.
Also take note of page loading speed (a ranking factor), as Google is obsessed with page speed.
Section 3: External SEO
What is external SEO all about? External SEO, more commonly known as off-page SEO is basically link building/marketing – Acquiring the most relevant backlinks from as many relevant high authority sites to achieve and maintain high rankings on the SRPs. A relevant backlink is an inbound link from one of the pages (with relevant meta information such as the title, description, etc.) of another similar-topic website.
Planning a successful link building campaign
In order to plan and execute a successful link building campaign for your site, you first need to understand that link building is a long and tedious process. One that requires skillfullness and extensive knowledge on the topic of SEO.
However if you persevere, stick to white-hat rules of SEO, animal-proof (Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird) your SEO campaigns by staying updated, you will eventually taste the fruit of success.
Fundamental off-page SEO concepts
Before we begin the link building process, let’s first go through and understand some fundamental concepts.
What is a backlink?
A backlink is an inbound or incoming link (hyperlink) to a particular website, referenced from another website. Search engines rely on links to crawl the web and evaluate the authority and relevance of millions of websites.
What is an anchor text?
An anchor text is the text you click on that takes you to a referenced url. i.e. (This sentence is an anchor text).
It is recommended that the anchor texts of inbound links be diverse (mix of target and non-target keywords, brand mentions, synonyms of target keywords, non-related words, etc.) and not all “exact match” to the target keyword that a site is aiming to rank highly for on the SRPs.
A link profile with majority of inbound links that have exact-match anchor texts looks very unnatural, and search engines will devalue these inbound links or even de-index the site.
Anatomy of a Strong Backlink
- High domain authority
- High PageRank
- High TrustRank
- Relevant co-citations
- Relevant page title
- Relevant content topic
- Target keywords in anchor text
- Placed in main content area
- Age of page
- Age of backlink
- Dofollow link
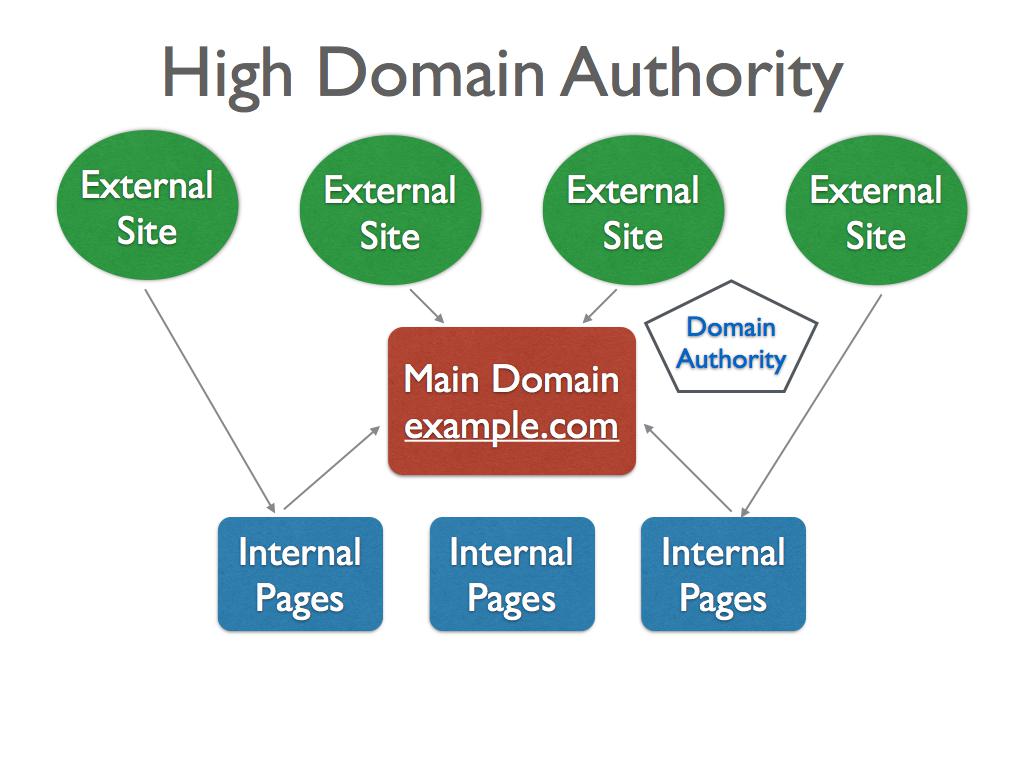
High Domain Authority
All inbound links pointing to a website’s main domain (www.example.com) as well as its internal pages contribute to the domain authority.
Getting a backlink from a high domain authority site is always valuable. Sometimes, that is all you need in order to get on the 1st page of Google for a target key phrase.
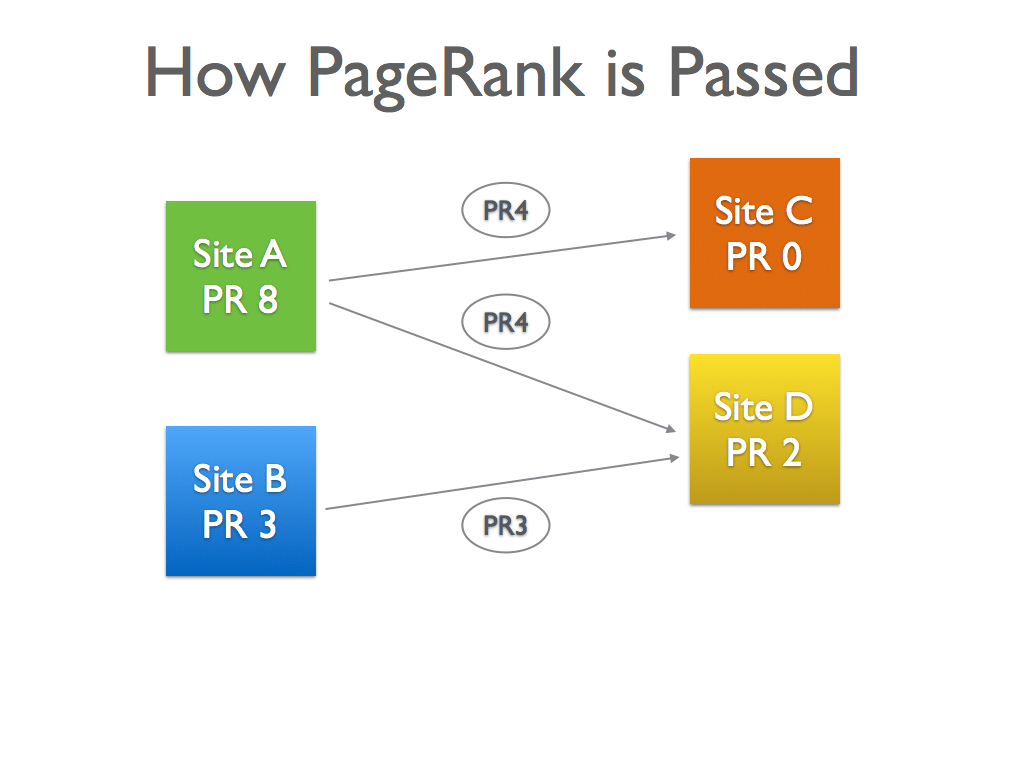
High PageRank
PageRank is only one of over 200 ranking factors which Google uses to calculate and decide which page should rank over another.
Inbound links pointing specifically to an internal page of a particular website contributes to the PageRank of the specific page.
However if a page of say PageRank 6 has two outgoing links, the outgoing PageRank is diluted into half (PageRank 3 each).
With everything else equal (i.e. Relevant page title, equal number of backlinks, etc.), a site with a higher PageRank will rank above the site with a lower PageRank.
High TrustRank
Sites that receive a lot of quality relevant inbound links are more trusted than sites that receive lots of inbound links from low-quality, spammy sites.
Getting a link directly from a very trusted site such as Entrepreneur.com will increase your site’s TrustRank tremendously. Obtaining a second-tier, third-tier, or fourth-tier link will also increase your site’s TrustRank but the value starts to drop the further it goes.
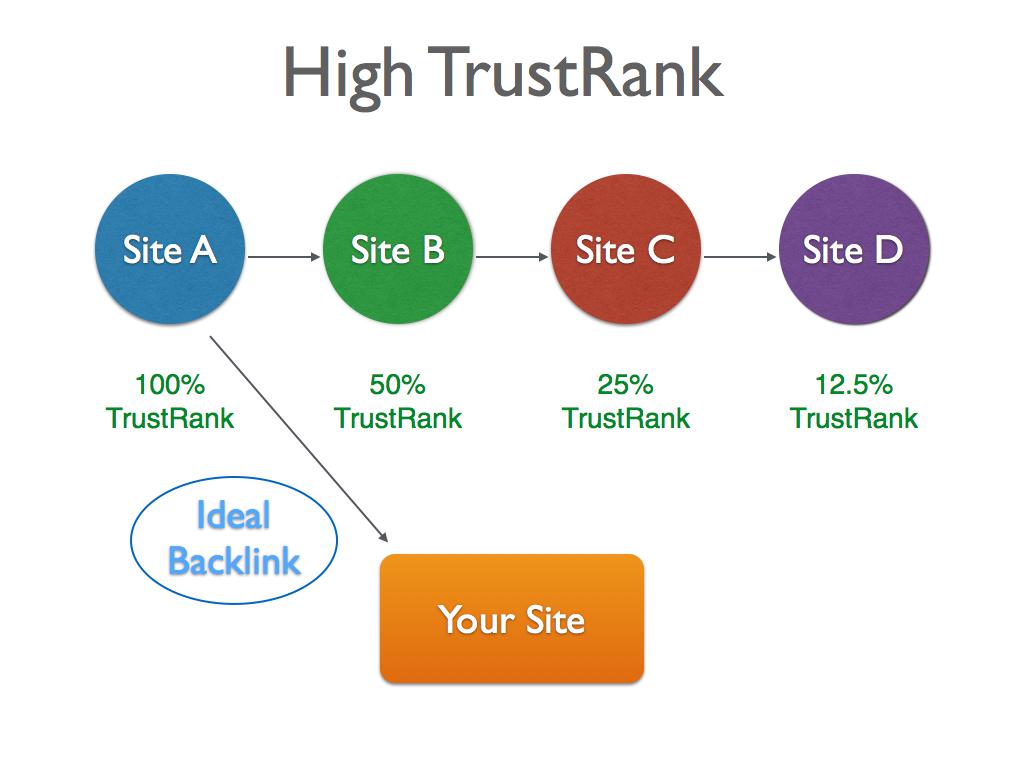
Let’s have a look at the following scenario:
Your website provides financial consultation and you are not able to get a link directly from Entrepreneur.com. However you’re able to obtain a third-tier link from one of the websites that Entrepreneur.com links to.
Entrepreneur.com => Financesite.com => Bizservices.com => Yourfinancialsite.com
100% TrustRank => 50% TrustRank => 25% TrustRank => 12.5% TrustRank
The above figures are made up and only used to demonstrate the point.
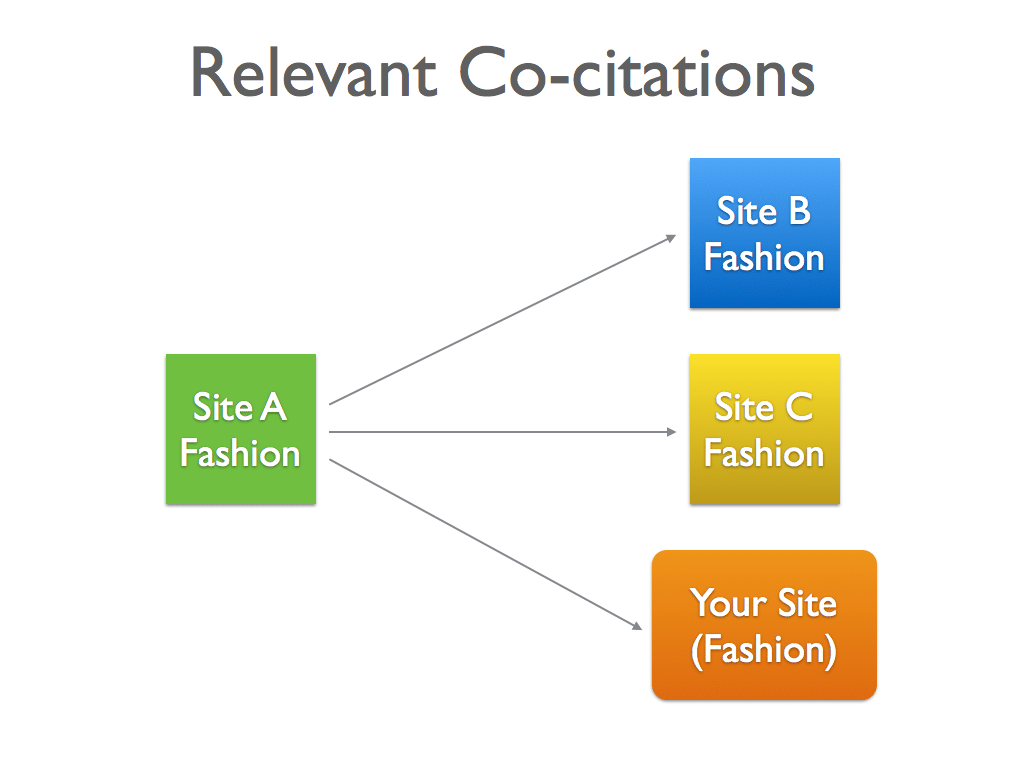
Relevant Co-citations
If you are getting inbound links from an external page (Page A) and it is linking to Page B and Page C which are both relevant to your site’s content topic, this is a strong signal to search engines that your site is relevant to that particular topic.
Relevant Page Title
The page title should summarise the page’s content topic. Or rather, the main content topic should reflect the title of the page. Search engines use the page title as an important ranking factor when it comes to displaying relevant search results to the user.
Relevant Content Topic
Similar to the above Relevant Page Title ranking factor, an inbound link from a page with relevant content topic to your site will increase your relevancy score.
Target Keywords in Anchor Text
The anchor text of a link is another ranking signal that search engines use. The wide-spread belief before the 2012 Google Penguin Update was that a keyword rich anchor text was a strong ranking factor.
As a result, many webmasters started over-optimising their inbound anchor texts by stuffing their target keywords in (exact match), in attempt to manipulate their rankings. Majority of the sites with over-optimised keyword-rich anchor texts who were hit by the update saw a big drop in rankings.
Post-Penguin, anchor texts should not be over-optimised. i.e. If you want to rank for “financial consultation”, your anchor texts shouldn’t all be “financial consultation”. There should be a good mix of different types of anchor text. It should sound natural as if someone were to mention your brand name in a conversion.
Here are a few examples of the different types of anchor texts a property/real estate website should have a good mix of:
Exact match – “Properties for sale”
Broad match – “List of properties for sale” or “Properties for sale in [country]”
Synonyms and related search terms – “Condos for sale” or “Private property for sale”
Brand mentions – “Realtoria Property Investment Firm”
Non-related – “visit this page” or “click here”
It’s good to have a couple of inbound links with exact match anchor text from high domain authority sites. Just make sure it looks natural and doesn’t make up the majority of your backlink profile.
Placed in Main Content Area
The location of the backlink is also an important factor. A footer link isn’t worth as much as a sidebar link, and a sidebar link isn’t worth as much as an editorial link in the main content section.
Age of Page
How long a page has been in Google’s index is also a ranking factor. Creating a website is getting much simpler. There has been an increasing number of fly-by-night sites and many webpages come and go frequently. Therefore the older the page, the more trustworthy it is (provided it is frequently updated).
Age of Backlink
Similarly, the older the backlink, the more TrustRank it gets.
Dofollow Link
Dofollow links are regular links without the rel=“nofollow” attribute in the HTML code and they allow PageRank or Link Juice to be passed on to the linked page.
Example of a regular dofollow link (allows PageRank to be passed on):
<a href=“http://example.com/”>anchor text</a>
Example of a nofollow link (doesn’t allow PageRank to be passed on):
<a href=“http://example.com/” rel=“nofollow”>anchor text</a>
While you’re in the process of acquiring dofollow links, you also want to obtain nofollow links.
Although you won’t get any PageRank from a nofollow link, the main reason you also want to include nofollow links in your link profile is that search engines are able crawl a nofollow link and read its anchor text.
Even though you don’t get any PageRank flow, you’d still be awarded points for relevancy. Not to mention a link profile with thousands of dofollow inbound links and without a single nofollow backlink looks a little fishy.
In a Nutshell…
Basically you want to acquire as many backlinks from other sites that are closely related to the topic of your site and your site’s internal pages.
You also want a diverse and natural-looking link profile;
Links from different types of sites (blogs, news sites, .edu & .gov sites, forums, directories, social media, etc…) with natural linking patterns, and a good mix of dofollow and nofollow links. (No heavily keyword-optimised anchor texts!)
External SEO is basically link building and creating social signals for search engines to determine the authority of your site as well as the context of your site. Here’s a guide to SEO link building you should really check out.
Do be careful however not to violate any of Google’s Content Quality Guidelines or participate in link schemes (A.k.a. Black-hat SEO) while in the “joyous” process of link building. As long as you avoid doing any Black-hat SEO, you’re most probably doing White-hat SEO.
If you’d like to learn practical techniques on how to search engine optimise your website internally (on-page SEO), as well as externally (off-page SEO), you may want to attend our hands-on SEO course in Singapore.
I hope this beginner’s SEO tutorial has given you a better understanding on the topic of SEO as a whole. To have a more holistic digital marketing landscape, we cover the core modules of Digital Marketing that includes :
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Content Marketing Strategy
- Search Engine Optimisation
- Digital Advertising
- Social Media Marketing
- Digital Marketing Analytics with Google Analytics
The completion of these modules will lead the learners to attain a Certified Digital Marketing Strategist Certificate. Please also feel free to browse our complete list of digital marketing courses held in-person in Singapore or online.
Dylan Sun is the Founder of Equinet Academy, a SkillsFuture Singapore WSQ-Accredited Digital Marketing training organisation. Passionate in all aspects of Digital Marketing and SEO, he extends his passion to helping people implement effective digital strategies to their businesses. Follow his blog at Equinet Academy to learn more about Digital Marketing.
I have read this all SEO tutorial and i found this such a valuable tutorial. Thank you very much.
Glad you found it valuable. You’re welcome!
Hello Dylan,
I appreciate your skills, this article is to much helpful for me. Although i was searching new SEO updates which clear my doubts.
Could you please suggest me the new off page activities which should need to do for website ranking method.
Regards
Astro Raj
http://srastrovastuconsultant.com/
Hello Astro,
Thanks for your kind comments.
For Off-page SEO, I suggest reading Paddy Moogan’s Link Building Book. Lots of great insights on link building.
nice
Awesome. A must-have for beginners.
Great article… Very understandable and systematical approach of writing and explaining. I find it very helpful.
Please suggest some stuff to learn about dofollow and nofollow links.
Thanks Emrit.
You may want to check out these sources:
https://moz.com/community/q/dofollow-and-nofollow-links
https://moz.com/blog/the-hidden-power-of-nofollow-links
Very Good…..!!!
Excellent search engine optimization guide for the beginners. All the content is very unique. Good work Dylan Sun.
Manshu Ydoxy
Seo Specialist
http://ydoxy.com/
Really helpful to us.thanks
I like this tut
Great Tutorial of SEO explained in a single page! Hatsoff
these were implemented on my site and ranked better.
Excellent guide for SEO beginners.Thank you so much.
Its really Understandable & easy to Learn about SEO.
Thank you so much.
Thanks for explaining SEO where I can actually understand it!! This is helpful for a beginner!
Thanks for sharing fruitful information about on page seo.
I have read this all SEO tutorial and I found this such a valuable tutorial.
Thank you very much.
Very nice tutorial for SEO beginner.
Thanks to share .
Excellent Article, Dylan!
Very useful indeed.
Thanks for being generous with your ideas.
Equinet Academy is truly impressive!
Thanks for stopping by to read, Rekha. Yes, we are passionate in helping businesses succeed. They are the lifeblood of the economy!
Thank you very much for this piece of info. I have always wanted to rank for long tail keywords and i have found all I think i should know in this post.
Thank you for the article Dylan it is useful for my further job training.
Thanks for reading Sai, glad it was useful for you.
Very well researched and written an in-depth article which will help a beginner to expert to consider some important tasks before asking Google for website/blog rankings.
great article, by this article i have got clear idea on seo.
Good information for SEO beginners. Keep it up!
Thanks for explaining SEO, It is really Understandable & easy to Learn about SEO where I can actually understand it!! This is helpful for a beginner! Thank you, Dylan.
Thanks for this amazing SEO guide for beginners.. I really love your post.. and it also help me to do seo in right way, here i got some new tricks..
Thanks .. Keep updating with such helpful blogs.
very informative for biginer
Thanks
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a combination of approaches that makes a website easier to find through search engines like Google and Yahoo. Search friendly websites are the ones you see on the first three pages of search results, and by just implementing search engine optimization basics you can greatly increase the chance of your website getting there.
Although there are ways of applying SEO at any time throughout the lifecycle of a website, we suggest thinking about SEO from the earliest stages of development. Otherwise, you might run into complications that make your website easier to rebuild completely than to fix. If you want to know what does SEO friendly mean, continue reading this article.
If you’re new to SEO, or if it isn’t your primary focus, you might be neglecting tactics that will really move the needle.
this is a very good topic for begginers that are want to take seo as her careers.very good thankyou
I applied some of your steps on our website Smoothstack, the result was really great. 😀 The guide you shared was really helpful and I hope you could continue creating great SEO article guidelines. Thank you
These steps are best for optimizing a website for search engine in a proper way. Thanks for sharing.
I am a beginner in the domain and a step by step SEO guide like this helped me a lot to understand about SEO. I applied some of your tips here and they really helped me. Thank you so much for sharing such a wonderful article with us, keep sharing such articles.
Thanks for sharing the knowledge on SEO, this is very useful for beginner bloggers like me.
Hello Dylan.
Superb Work…
I want to ask one question that Is there any Google Algorithm update related to website content. Because my website ranking suddenly drops. I searched for it but does not get a suitable answer to this. Can you help me out…
Waiting for your reply.
Thanks
Hi Jatin,
This is most likely due to the May 2020 update. More details here https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-may-2020-update-analysis/366740/
Thanks for this amazing SEO guide for beginners. I love your post—it helps me do SEO the right way and I’ve learned new tricks. Keep updating with such helpful blogs. Thanks!