What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is the practice of increasing a website’s visibility or ranking position on the organic or natural search engine results pages.
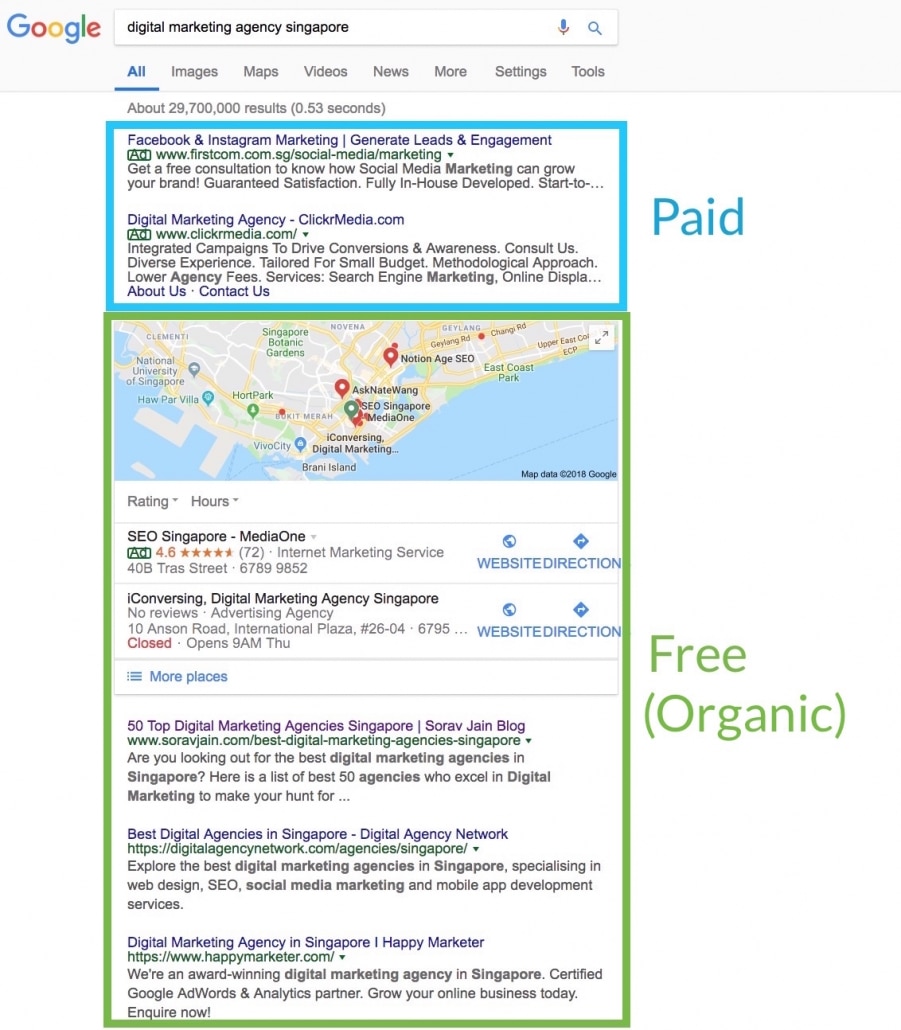
Every time you perform a search on Google, Google returns two types of search results: Paid search results, and organic search results.
Unlike the paid search results (pay per click model) which is managed by Google AdWords, SEO is the process optimising a website to rank on top of the organic search results
To get your website to show up on the paid search results on Google, you need to have a Google Ads account set up and be ready to pay a certain amount for every click you receive. This marketing technique is known as “SEM”. We compare SEO and SEM in this article.
In this article however, we’ll be focusing on SEO which refers to the process of increasing a website’s rankings on the organic search results. This is where you won’t be paying for any clicks you receive from Google.
But first, how does Google return over 29 million results for one search query? How do they even discover the billions of webpages on the internet? One of the ways Google achieves this is by sending out robots a.k.a. search engine spiders to crawl the web. When a search engine spider crawls a webpage, it downloads the content and stores it in Google’s indexes (huge gigantic servers that store and retrieve data).
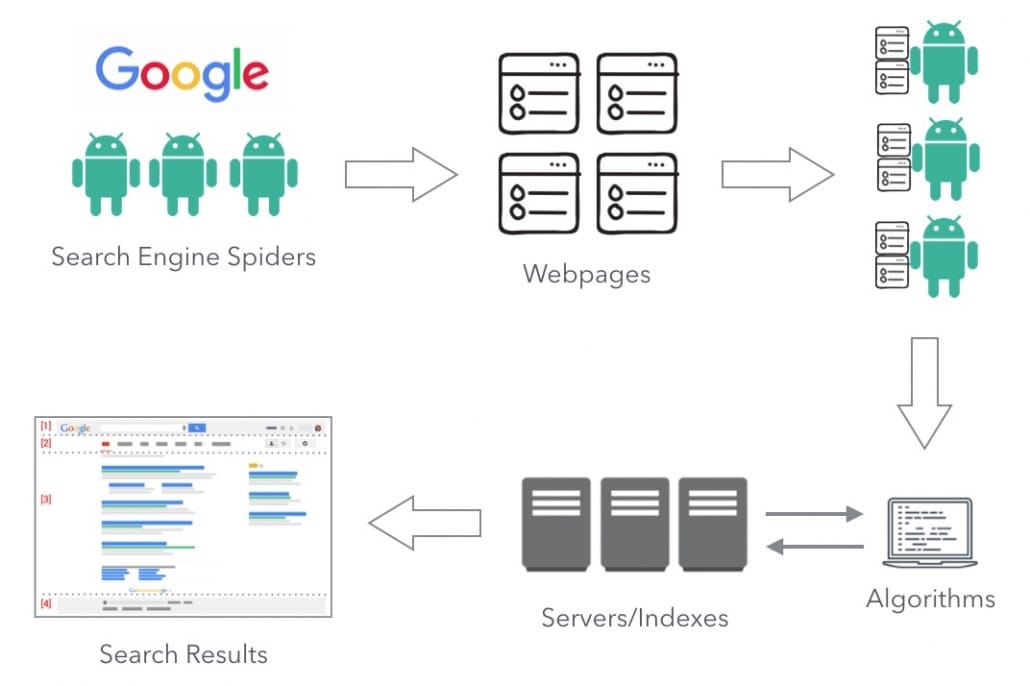
So, before you can even rank anything on Google, the first thing you obviously need is a website.
We don’t know exactly what every ranking factor is and the relative importance of each. But what we do know is that in general, pages that rank highly on Google display the following traits:
- Relevant to the search intent – Has to answer the question or search query
- Provide useful information to the searcher – Content is better than most pages that talk about the same thing
- Target keywords are included on the page – In the SEO meta tags, text body, and images
- Original and unique – Not plagiarised or duplicated
- Strong off-page signals – Has authoritative websites linking to it
Why is SEO Important?
SEO is important for the following reasons:
- Inbound marketing channels like SEO have a higher conversion rates than outbound channels – 3.82% compared to 2.98% (paid), according to a report by Marketo
- SEO has 20 times more traffic opportunity than PPC
- Ranking high on Google builds trust and credibility
- Organic web traffic is free
- Long term benefits – consistent traffic and conversions
- SEO can help you maximise your customer touch points, increasing the chances of sales – it takes 6 to 8 touch points to generate a viable sales lead.
In Singapore, Google has over 90% of marketshare among other popular search engines such as Bing and Yahoo!. As such, we will be focusing on Google SEO in this article.
To achieve top rankings for your target search terms, an SEO practitioner needs to be well-versed in the following disciplines:
- Keyword research
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Local SEO
- International SEO
How Does SEO Work?
SEO typically works in 4 phases.
Phase 1: Keyword Research
This is the first phase where you discover the keywords or search terms your target audience uses to find information online.
Phase 2: On-Page SEO
This is the part where you ensure the keywords your target audience uses are also mentioned on your webpages. Other important aspects of on-page SEO include making sure your content is useful and relevant to what the user is searching for, providing a good user experience, and technical SEO, which includes ensuring your website loads quickly and is free from technical errors, such as not being mobile-optimised.
Phase 3: Off-Page SEO
In order for users to trust your brand and for search engines to rank it highly on the search results pages, you need to build more brand awareness and grow your authority.
This is referred to as off-page SEO. Off-page SEO techniques include getting other websites to mention your brand and hyperlink back to your website (also known as backlink building). It also involves growing your brand presence on social media and garnering positive reviews around the web.
Phase 4: SEO Analytics
In the final phase, you review the ranking position of your website for all your target keywords and focus on improving their positions.
Keyword Research
Keywords, sometimes referred to as search terms, search queries, and key phrases, are the foundation of Search Engine Optimisation. Take away this element and search engines become redundant.
Keyword research is the process of selecting keywords based on market research (e.g. using a keyword research tool such as Google Keyword Planner, analysing existing keyword data via a web analytics software) to optimise a website’s search engine rankings for.
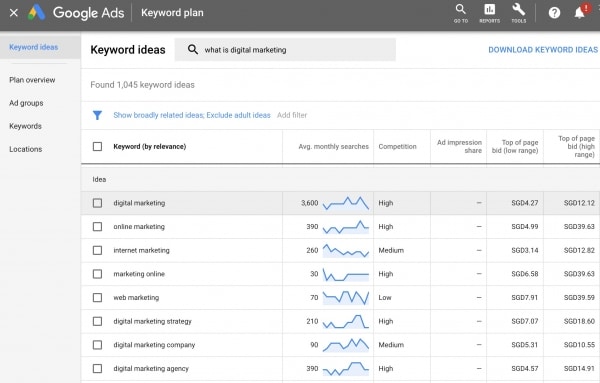
Once you have chosen your target keywords (i.e. built your keyword list), the next step is to populate your website with the selected keywords.
Further reading:
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the practice of optimising a website and its individual webpages to improve its search engine rankings. It can be further divided into two parts:
- Non-technical on-page SEO
- Technical on-page SEO
Some activities of non-technical on-page SEO include inserting keywords into editorial copy, tailoring content to satisfy the intent of the searcher, and organising website content architecture in a silo-ed fashion to deliver a good user experience (in terms of navigating around your website).
For technical on-page SEO, some of the activities include modifying webpage meta tags (e.g. title tags, meta description, and rel canonical tags), developing mobile-friendly pages with AMP content, implementing SEO-related markups (e.g. Schema.org markup, rel=nofollow, and rel alternate hreflang), and dealing with duplicate content (e.g. rel canonical tags, redirect, and noindex).
Basically, both technical and non-technical on-page SEO aim to make a website search engine friendly, which increases the chances of it ranking higher on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Further reading:
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to techniques and activities carried out externally from the website to improve its search engine ranking position. Some of the activities include:
- Content marketing
- Link building
- Online PR for brand exposure
- Earning brand mentions
- Building an online community (e.g. on social media platforms, blogs, and forums)
- Garnering reviews
- Local citation building
All the above off-page activities come down to establishing an online brand presence, which boost brand recall and build backlinks to a website. And we all know that backlinks play a major role in influencing a website’s search engine rankings.
Further reading:
How to Build Links to Your Website – A 4-Step Link Building Strategy
Local SEO
Local SEO refers to the practice of boosting the visibility of a local brick and mortar business’s listing on the local search results.
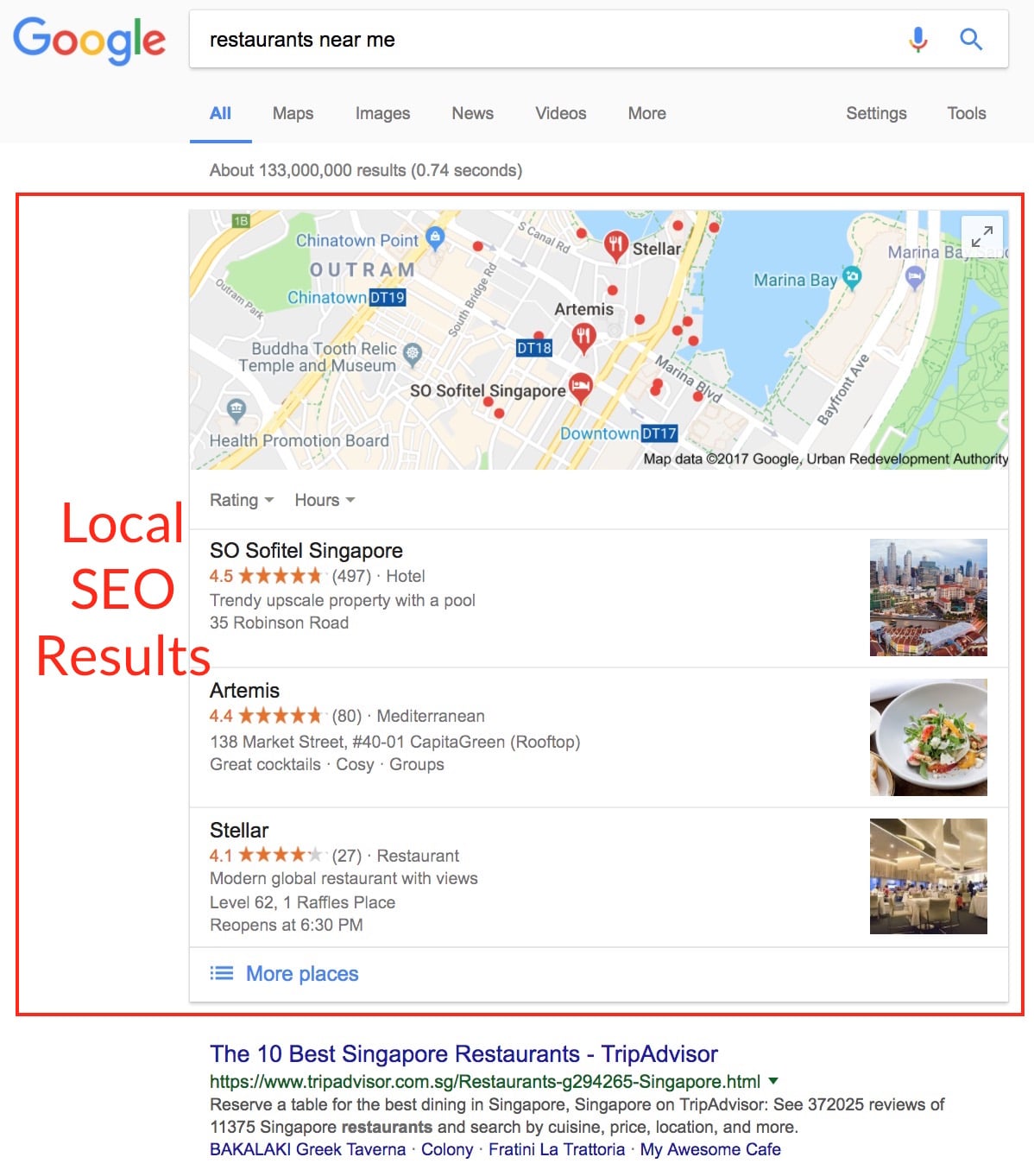
- Local citation building: Submitting your company details (business name, address, phone number) to local business directories.
- Garnering reviews: Getting your customers to leave reviews on your Google MyBusiness page.
- Local link building: Acquiring backlinks from local websites (e.g. getting websites, journalists, and local influencers/bloggers to hyperlink to your website)
International SEO
International SEO refers to the practice of optimising a website to increase its global presence on international search engine domains.
It involves segregating content by language and currency (if applicable), based on various target audiences, into different country code top level domains (CCTLDs), subdomains, or sub directories.
For example, an online fashion retailer e.g. www.fashionxyz.com may want to expand its international search presence to Australia and Japan. It creates two new websites on the CCTLD domains www.fashionxyz.com.au and www.fashionxyz.jp and tailors its content to the local languages of both countries. This helps Google and other search engines to rank the correct version of the website in the right country.
White Hat Vs. Black Hat SEO
Unfortunately, in this competitive industry, many marketers resort to questionable or shady techniques to try and manipulate their organic search engine rankings. This is known as black hat SEO.
Examples of black hat SEO include keyword stuffing and cloaking, where the keywords are mentioned repeatedly on a webpage and even made invisible to web users.
Another example of a black hat SEO technique is writing a ton of low-quality blog articles and publishing them on the same domain to trick search engines into thinking the website is an established content hub, when it really is the opposite.
White hat SEO on the other hand, is the more effective approach in the long run. It gears toward providing a great experience for site visitors through creating high quality content that answers each search query in the best way possible.
A great brand with great content and great products will grow its reputation in the online space naturally. This will result in more positive reviews, brand mentions, and backlinks off-site, sending positive ranking signals to search engines. At the end of the day, search engines were created for humans and will always strive to improve for us all.
Google’s mission is to organise the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. Its vision is to provide an important service to the world, which is to – instantly deliver relevant information on virtually any topic.
This would not have been possible without the advent of search engine algorithms.
According to Google, an algorithm is a process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer.
Google has dozens of algorithms programmed to determine the relevance and quality of a content piece to a given search query, and these algorithms are improved upon several times a day.
Therefore, trying to game search engine giants like Google is a constant uphill battle, and you will be better off optimizing your content for humans, which was what search engines were built for in the first place.
What Does it Take to Do SEO?
Search Engine Optimisation or SEO can be a tedious process and requires someone (and sometimes a team) with a diverse set of skills which includes but not limited to:
- Web development knowledge – for technical on-page SEO implementation
- Good content writing and copywriting skills – With the rapid advance of search engine algorithms and natural language processing, there is no room for poor quality content to rank on top
- Excellent online PR skills and content marketing skills – to build off-page SEO signals such as link building
- Good project management skills – SEO is highly competitive and requires someone who can get things done
If you found this post helpful, you may also find the following resources helpful in furthering your SEO knowledge.
Further Reading:
A-Z Glossary of SEO Terms and Definitions
SEO Tutorial Step-By-Step Guide
Sign up for an SEO course:
WSQ Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Certification Course
If you prefer a more advanced SEO class, we offer a WSQ Advanced Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Course as well.
We also offer an array of digital marketing courses taught in-person in Singapore or online.
Never Miss a Post
Receive the latest blog articles right into your inbox.
Dylan Sun
Dylan Sun is the Founder of Equinet Academy, a SkillsFuture Singapore WSQ-Accredited Digital Marketing training organisation. Passionate in all aspects of Digital Marketing and SEO, he extends his passion to helping people implement effective digital strategies to their businesses. Follow his blog at Equinet Academy to learn more about Digital Marketing.




Reader Interactions
2 Comments
I am having my website and was thinking to start SEO for that. But how should I? was the biggest question for me. I was not knowing much about SEO so I started self-learning about SEO and came across your article. I got all the information about SEO from this article. I will start SEO for my website soon.
Thank you….!!!
Hey,
Thanks for explaining what is SEO marketing and how it works. The
information with search engine result page image is quite impressive.
I watched the video also. International SEO was something new concept
for me. The four phases of SEO are very informative.