SEO, SEM, and PPC. These terms have been used interchangeably for the longest time, but are they the same?
This article aims to iron out the definition of each discipline and provide you with a clearer understanding of the features, differences, pros, and cons.
What are SEO and SEM, and What Exactly is PPC?
SEO or Search Engine Optimization, is optimizing a website to rank prominently on the organic search results. For example, if you run a bakery and want more people to find your website when they search for “best cupcakes in Singapore,” you might optimise your site by adding relevant keywords, improving website speed, and earning backlinks from food blogs. Over time, your website could appear on the first page of Google without paying for ads.
SEM or Search Engine Marketing is a subset of digital advertising, associated with targeting a website to rank on the paid search engine results pages. For instance, if you own a car rental business and want to appear at the top of Google when someone searches for “affordable car rental in London,” you can bid on that keyword through Google Ads. Your website will then show up in the sponsored section of the search results, marked as an ad.
PPC or Pay Per Click refers to the buying model in which advertisers pay a fee for every click their ad receives. A common example is when an e-commerce store runs a Google Ads campaign to “buy running shoes online.” Every time a user clicks on their ad, the store pays a small fee, even if the user doesn’t make a purchase. This model is also widely used on social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, where brands run sponsored posts and pay for every click on their ads.
Based on the above definitions, SEO and SEM exist within the umbrella term “Search Marketing”. While PPC is a buying model that is commonly and inaccurately used interchangeably with SEM, it isn’t wrong to say that SEM and PPC co-exist within the same subset of Digital Advertising – Search Advertising.
Note that other subsets of Digital Advertising include:
- Display Advertising
- Social Media Advertising
- Programmatic Real-Time Bidding
- Mobile Advertising
The Main Difference Between SEO and SEM
The main difference between SEO and SEM is that the former is a method of ranking a website on the organic search results, while the latter is based on a pay-per-click model of displaying text ads above the organic search results.
To better illustrate this, let’s put on the hat of a Marketing Executive of a B2B organic food supplier.
Your clients are looking for organic products on Google, and they’re typing in search terms such as “organic food”.
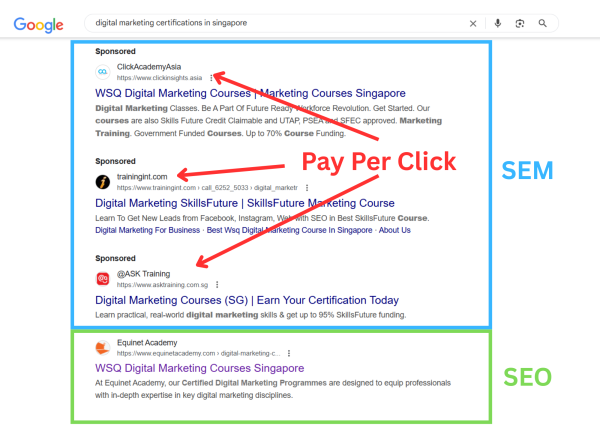
Example of Pay Per Click buying Model in the search channel, organic search and paid search results
To be visible and potentially acquire clients at this crucial moment, your website needs to be ranked highly in paid search results, organic search results, or, in the best-case scenario, both.
To rank on the paid search results, you set up your ads and target keywords on Google AdWords. Within a day, your company website ranks in the top 4 positions of Google whenever a potential client searches for your target keywords (ie, “organic food suppliers”).
However, you must pay Google AdWords a fee every time a user clicks on your ad. That’s because Google AdWords charges advertisers based on a PPC model.
After evaluating your costs vs results, you realize you may not be able to maintain your budget for the long term as more and more competitors bid and compete for the same target keywords.
You decide to invest in an SEO strategy to rank your website on the organic search results, instead, where clicks don’t cost you anything.
The Similarities and Differences Between SEO and SEM
We know that both SEO and SEM are subsets of search marketing that coexist in the same channel of search. We also know that we have to pay a fee for every click for SEM traffic, while we pay nothing for clicks from SEO efforts.
That said, here are the similarities and differences between SEO and SEM.
Similarities
- SEO and SEM both co-exist on the same channel – The search channel
- Both SEO and SEM are intent-based marketing
- Being visible on either SEM or SEO search results boosts brand awareness, regardless of whether you get any clicks
Differences
- SEM search results (up to 4 paid search results) appear above SEO search results (up to 10 organic search results)
- SEM search results are demarcated with an “Ad” symbol, while SEO search results aren’t
- SEO search results have different features from SEM search results, such as featured snippets, while SEM results have ad extension features
- SEM drives paid traffic while SEO drives organic (non-paid) traffic
- SEO efforts take a longer time to show results than SEM efforts
SEO vs SEM – Pros and Cons
The pros and cons of SEO and SEM as outlined in the comparison table below.
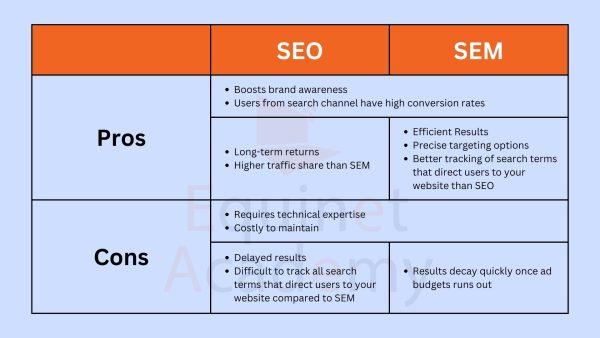
Pros and cons of seo and sem comparison table
When your website ranks for multiple search terms, it increases brand visibility, even if users don’t click on it. Search-driven traffic also tends to have higher conversion rates because SEO is an intent-based marketing channel, meaning users actively search for solutions, making them more likely to convert.
While SEO is a long-term investment, it provides sustainable results over time. It can take weeks or months to see noticeable improvements, but once your site ranks highly, it maintains visibility for a longer period. In contrast, SEM (Search Engine Marketing) delivers immediate results but requires ongoing ad spend. The moment your budget runs out, your ads stop appearing. Additionally, organic search results typically receive more clicks than paid ads, though this varies by industry and search terms.
With SEM, you can launch a Google Ads campaign and start driving traffic within an hour, making it an excellent option for quick results. It also offers precise targeting capabilities, allowing you to choose when and where your ads appear, including specific time slots, geographic locations, and ad placements. Unlike organic search, Google Ads provides detailed insights into the exact search terms users typed before clicking your ad, whereas organic search data is more limited.
For example, if you target the keyword “organic food Singapore”, and a user searches for “organic foods Singapore”, your report will capture the variation, helping you refine your strategy.
Both SEO and SEM require technical expertise to maximise performance and ROI. Managing these strategies effectively can be challenging and expensive, making it difficult to maintain a skilled in-house team. As a result, many businesses choose to work with digital marketing or SEO agencies to handle their campaigns more efficiently.
Both SEO and SEM require technical and platform expertise to outperform your competitors and generate a positive ROI. This means it can be difficult and costly to hire in-house specialists to execute and oversee your campaigns. Because of this, the option of hiring a digital marketing agency or an SEO agency is a rather popular choice for marketing departments.
Should You Do SEO or SEM?
It depends. Several factors could affect your decision whether to do only SEO, SEM, or both.
For instance:
- Short customer lifecycle: If you’re launching a promotional product marketing campaign with a short buying cycle (eg, 1 month), you won’t have the time to wait for your SEO efforts to boost your website to page 1. You need to execute an SEM campaign and get on top of the search results pages asap.
- You want to maximise traffic from the search channel: Studies have shown that ranking on both the paid and organic search results pages results in incremental clicks overall. In this case, you want to run both SEO and SEM campaigns simultaneously.
- Competition on paid search is over the roof: If a click costs you $58.64 and your profit margin is negative, you shouldn’t be doing SEM.
- You want to test the market: Since SEM can get you visibility very quickly, you can test which keywords convert better. After analysing your performance, you can then direct your focus to keywords that convert better in your SEO campaign.
SEO vs. SEM: How Long Does It Take to See Results
When it comes to digital marketing, understanding the timeline for results is crucial, especially when comparing SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) and SEM (Search Engine Marketing). While both strategies aim to increase visibility and drive traffic to your website, the speed at which they produce results differs dramatically.
SEO: A Long-Term Strategy with Delayed Gratification
One of the most significant differences between SEO and SEM is the time it takes to see results. SEO is a long game. Building organic visibility takes time, often a lot of it, particularly if your website is new or lacks backlinks.
A well-known analysis found that it takes, on average, two years for a website to rank on the first page of Google. Many of the pages that dominate the top spots today were originally published more than three years ago. This doesn’t mean that all SEO efforts are fruitless in the short term, but it does highlight the need for patience.
That said, targeting long-tail keywords and consistently implementing SEO best practices can accelerate your progress. Some websites start seeing modest traffic increases within a few months of optimisation, even with minimal domain authority.
A real-world example comes from the early days of Backlinko. Launched in 2013 with virtually no domain authority, the site began to see organic traffic within a few months, thanks to a laser-focused SEO strategy. However, it still took years for the site to build the kind of rankings and organic traffic that now define its success.
SEM/PPC: Fast Results with a Learning Curve
In contrast, SEM—particularly when focused on Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising—delivers far faster results. You can launch a Google Ads campaign in the morning and start driving traffic and conversions by the afternoon. This immediacy is one of the primary benefits of PPC and a compelling reason why businesses looking for quick wins often turn to paid search.
However, rapid traffic doesn’t automatically translate to immediate profit. While PPC offers instant visibility, achieving a positive ROI typically requires months of testing, refining ad copy, adjusting bids, and optimising landing pages. The learning curve can be steep and ongoing, particularly in competitive niches.
Speed vs. Sustainability
The choice between SEO and SEM often comes down to your goals and timeline:
- If you’re in it for the long haul and want sustainable, cost-effective traffic over time, SEO is the way to go.
- If you need immediate visibility and are prepared to invest in ongoing optimisation, SEM/PPC can deliver quicker wins.
In many cases, the most effective digital marketing strategies incorporate both SEO and SEM, allowing you to reap short-term gains while building long-term growth.
Choosing between SEO, SEM, or both depends on your industry, goals, and timeline. Instead of guessing, make data-driven decisions that maximise your marketing impact.
- Want to rank higher on Google and drive long-term organic traffic? Our hands-on SEO course teaches you proven strategies to improve your search rankings effectively.
- Need immediate traffic and fast results? Learn how to create high-performing ads with our Google Ads course, where you’ll master setting up and optimising SEM campaigns from scratch.
- Explore more ways to level up your digital marketing skills! Browse our comprehensive range of courses, available in person in Singapore or online. Start learning today!
Never Miss a Post
Receive the latest blog articles right into your inbox.
Dylan Sun
Dylan Sun is the Founder of Equinet Academy, a SkillsFuture Singapore WSQ-Accredited Digital Marketing training organisation. Passionate in all aspects of Digital Marketing and SEO, he extends his passion to helping people implement effective digital strategies to their businesses. Follow his blog at Equinet Academy to learn more about Digital Marketing.
Keep Learning
10 Best Keyword Research Tools for your SEO and Content Marketing Efforts
Check the best keyword research tools for a successful SEO strategy.






Reader Interactions
2 Comments
I personally found this article very interesting. The similarities, as well as differences between seo and sem are well explained in this very blog. I had my doubts earlier, but now I’m pretty much clear about it. I would definitely recommend this to my fellow colleagues.
Loved the article , it was short and crisp and the important aspects about SEM PPC and SEO were highlighted. Found it very helpful . THANKYOUU!